Synthetic data generation¶
Synthetic data generation is essential for modern data science and analytics, enabling teams to work with realistic datasets while protecting privacy and accelerating development cycles.
Dataiku provides three powerful approaches to creating synthetic tabular data:
Privacy-Preserving Synthesis: Uses differentially private algorithms (DP-CTGAN, PATE-CTGAN, MWEM) to generate synthetic records from sensitive data. These algorithms provide formal privacy guarantees, ensuring that synthetic outputs cannot be traced back to individuals while preserving statistical properties for analysis.
Universal Data Generator: Enables declarative creation of synthetic datasets from scratch using statistical distributions, categorical sampling, Faker providers, and advanced correlation modeling. This approach is ideal for creating test data, developer sandboxes, and controlled datasets for model validation.
Classification Target Oversampling: Rebalances binary or multiclass classification datasets using one of three methods: Conditional Variational Autoencoder (CVAE), SMOTENC, or ADASYN.
All models are implemented using industry-standard libraries: SmartNoise for differential privacy, NumPy for statistical distributions, and Faker for realistic fake data generation.
Setup¶
These approaches are provided by the “Synthetic Data Generation” plugin, which you need to install.
Usage¶
Once setup, you can access new recipes in any project:
Create or open a Dataiku project.
In the Flow, click on the +Recipe button.
Navigate to the Synthetic Data Generation section.
Choose between: - Generate Synthetic Data: For privacy-preserving synthesis from sensitive data - Universal Data Generator: For creating synthetic datasets from scratch - Oversample Classification Targets: For rebalancing classification targets by generating synthetic minority-class rows (CVAE, SMOTENC, or ADASYN)
Why Synthetic Data Matters¶
Privacy budget amortization: Differential privacy spends a fixed ε budget whenever real data is queried. Generating a differentially private synthetic dataset consumes that cost once, after which unlimited analyses on the synthetic output incur no additional privacy loss thanks to the post-processing property of differential privacy.
Exploratory data analysis: Analysts need to inspect formats, ranges, and correlations before building models. Synthetic datasets provide a privacy-safe proxy for schema discovery, cleaning, visualization, and quick validation prior to running protected pipelines.
Data democratization: Regulated sectors often keep raw records inside secure enclaves. Synthetic datasets can be exported because they provably avoid mapping back to individuals, enabling teams with lower clearances—or external vendors—to collaborate without touching private records.
Developer sandboxes: Engineering teams rely on debuggable datasets. Synthetic outputs support writing SQL/Python pipelines and reproducing errors locally before shipping code to restricted environments, creating a safe iteration loop that mirrors the private data structure.
Generate Synthetic Data (Privacy-Preserving)¶
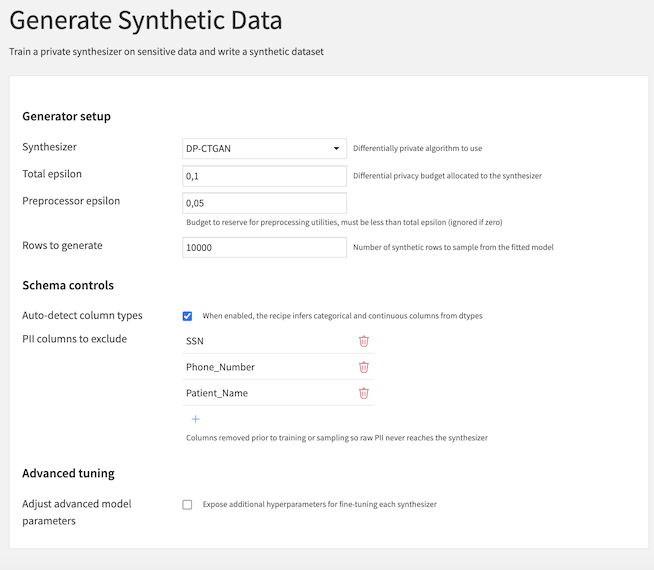
This recipe enables you to train a differentially private synthesizer on sensitive data and generate synthetic records that preserve statistical properties while protecting individual privacy. The recipe supports three state-of-the-art algorithms:
For class-imbalance workflows on classification targets, see Oversample Classification Targets below.
Synthesizer Options¶
DP-CTGAN: Differentially Private Conditional Tabular GAN. A generative adversarial network that learns to generate synthetic tabular data with strong privacy guarantees.
PATE-CTGAN: Private Aggregation of Teacher Ensembles CTGAN. Uses an ensemble approach to provide privacy through consensus mechanisms.
MWEM: Multiplicative Weights Exponential Mechanism. A lightweight algorithm that works well for datasets with moderate dimensionality.
Parameters¶
Synthesizer: Differentially private algorithm to use (DP-CTGAN, PATE-CTGAN, or MWEM)
Total epsilon: The privacy budget allocated to the synthesizer (lower values = stronger privacy but potentially lower utility)
Preprocessor epsilon: Budget to reserve for preprocessing utilities, must be less than total epsilon (optional, ignored if zero)
Rows to generate: Number of synthetic rows to sample from the fitted model
Auto-detect column types: When enabled, the recipe infers categorical and continuous columns from dtypes
Continuous columns: Columns forced to continuous handling; all remaining columns will be treated as categorical (only visible when auto-detect is disabled)
PII columns to exclude: Columns removed prior to training or sampling so raw PII never reaches the synthesizer
Adjust advanced model parameters: Expose additional hyperparameters for fine-tuning each synthesizer
Output¶
The recipe produces a synthetic dataset that:
Preserves statistical relationships from the original data
Provides formal differential privacy guarantees
Can be shared without exposing individual records
Supports downstream analysis and model development
Evaluating Synthetic Data Quality¶
You can assess the utility of your generated synthetic dataset in two ways:
Distribution comparison: Use the Model Evaluation Store to compare data drift between the synthetic and original datasets, ensuring statistical properties are preserved.
Model performance: Train a predictive model on the synthetic data and evaluate its performance on the original dataset to validate real-world utility.
Oversample Classification Targets¶
This recipe is designed for classification datasets where one or more classes are underrepresented. It supports three oversampling methods:
Conditional Variational Autoencoder (CVAE): Learns a generative model for minority-class synthesis.
SMOTENC: Synthetic nearest-neighbor interpolation with native support for categorical features.
ADASYN: Adaptive synthetic sampling focused on hard-to-learn minority regions.
Parameters¶
Common parameters¶
Target column: Classification target column to rebalance (binary or multiclass)
Oversampling method: Choose CVAE, SMOTENC, or ADASYN
Max synthetic multiplier: Caps generated rows to a multiple of the original dataset size
Max categories per categorical column: Keeps the top N categories and groups remaining values into
__OTHER__Random seed: Seed for reproducibility
CVAE-specific parameters¶
Latent dimension: Size of the latent CVAE representation
Hidden dimension 1: Width of the first hidden layer
Hidden dimension 2: Width of the second hidden layer
Dropout: Dropout rate applied in model layers
Max rows for training (optional): Maximum rows sampled for CVAE training when the dataset is large
Epochs: Number of training epochs
Batch size: Mini-batch size for training
Learning rate: Optimizer learning rate
Weight decay: L2 regularization term for optimizer
KL beta: Weight applied to KL-divergence in the CVAE objective
KL warmup epochs: Number of epochs used to ramp up KL contribution
Neighbor-method parameters¶
SMOTENC k-neighbors: Number of neighbors used by SMOTENC (SMOTENC mode only)
ADASYN n-neighbors: Number of neighbors used by ADASYN (ADASYN mode only)
Output¶
The recipe produces an output dataset that:
Keeps all original input rows
Appends synthetic minority-class rows when rebalancing is needed
Adds a
synthesizedboolean column to distinguish generated rows from original rows
Universal Data Generator¶
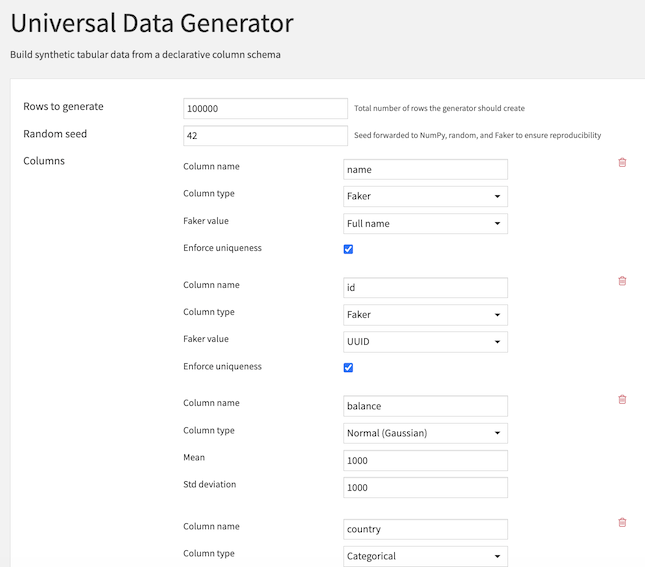
This recipe enables you to build synthetic tabular data from scratch using a declarative column schema. It combines statistical distributions, categorical sampling, date generation, Faker providers, and advanced correlation modeling to create realistic synthetic datasets.
Configuration¶
The recipe requires the following inputs:
Rows to generate: Total number of rows the generator should create
Random seed: Seed forwarded to NumPy, random, and Faker to ensure reproducibility
Columns: Iteratively describe each column to generate
Column Types Reference¶
The Universal Data Generator supports two main categories of columns: Independent (standalone) and Dependent (correlated with other columns).
Independent Column Types¶
Normal (Gaussian)¶
Generate numeric values following a normal distribution.
Parameters:
Mean: Center of the distribution (default: 0.0)
Std deviation: Spread of the distribution (default: 1.0)
Uniform¶
Generate numeric values uniformly distributed across a range.
Parameters:
Minimum: Lower bound (default: 0.0)
Maximum: Upper bound (default: 1.0)
Random Integer¶
Generate integer values uniformly distributed across a range.
Parameters:
Minimum: Lower bound (default: 0)
Maximum: Upper bound (default: 100)
Categorical¶
Generate categorical values from a predefined set of choices.
Parameters:
Category choices: List of possible values
Category weights: Optional probabilities for each choice (must sum to 1)
Date¶
Generate random dates within a specified range.
Parameters:
Start date: Beginning of the date range (default: 2023-01-01)
End date: End of the date range (default: 2024-01-01)
Faker¶
Generate realistic fake data using the Faker library.
Parameters:
Faker value: Choose from definitions:
Full name, First name, Last name
Email, Free email
Phone number
Street address, City, Country
Company, Job title
IBAN, UUID, License plate
Enforce uniqueness: Ensure all values are unique (optional)
Dependent Column Types¶
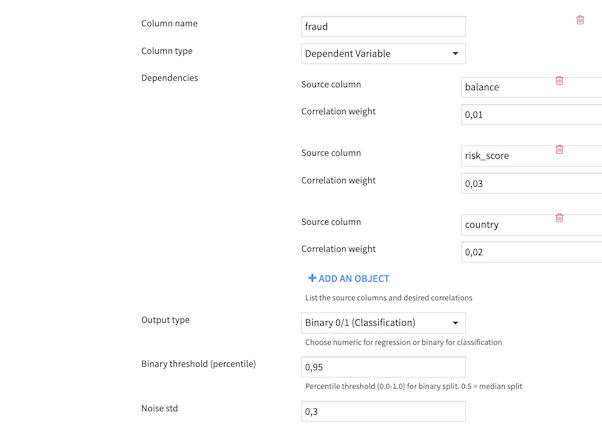
Numeric Output (Regression)¶
When selecting numeric output, you can optionally rescale the generated values to a specific range.
Additional Parameters:
Rescale output: Enable range rescaling (optional)
Minimum value: Lower bound of rescaled range (default: 0.0)
Maximum value: Upper bound of rescaled range (default: 100.0)
Binary Output (Classification)¶
When selecting binary output, the continuous correlated values are converted to 0/1 using a percentile-based threshold.
Additional Parameters:
Binary threshold (percentile): Controls class balance (0.0-1.0)
0.5 = 50/50 split at median
0.3 = 30% class 1, 70% class 0
0.7 = 70% class 1, 30% class 0