HTTP proxies¶
When to configure HTTP proxies¶
You may want to configure your DSS instance to work with HTTP proxies when either of the following scenarios applies:
Your users need to go through a (direct) proxy to reach the DSS interface. In this scenario, your proxy must support the WebSocket protocol, and allow long-lived WebSocket connections.
DSS is installed on a server without direct outgoing Internet access and a proxy is required to reach external resources. For configuration steps, visit Configuring a global proxy to allow DSS to access external resources.
Note
This must not be confused with the ability to deploy DSS behind a reverse proxy. See Using reverse proxies for more details.
About WebSocket¶
DSS uses the WebSocket protocol for parts of its user interface. The WebSocket protocol may not be supported by all HTTP proxies.
Ensure any direct or reverse proxy configured between DSS and its users correctly supports WebSocket, and is configured accordingly.
At the time of writing, this includes:
nginx version 1.3.13 and above (see nginx websocket proxying)
Apache 2.4.5 and above (with mod_proxy_wstunnel)
Amazon Web Services Application Load Balancer
See Websockets problems for related details and troubleshooting advice.
Configuring a global proxy to allow DSS to access external resources¶
Routing all requests initiated by the DSS backend through a proxy¶
To route all requests initiated by the DSS backend through the proxy, you’ll need to configure the HTTP Proxy settings in the Administration menu.
Go to the Administration menu, select the Settings tab, and then open the Misc. panel.
In HTTP proxy, supply the proxy host and port.
Optional: If the HTTP proxy requires authentication, supply the username and password.
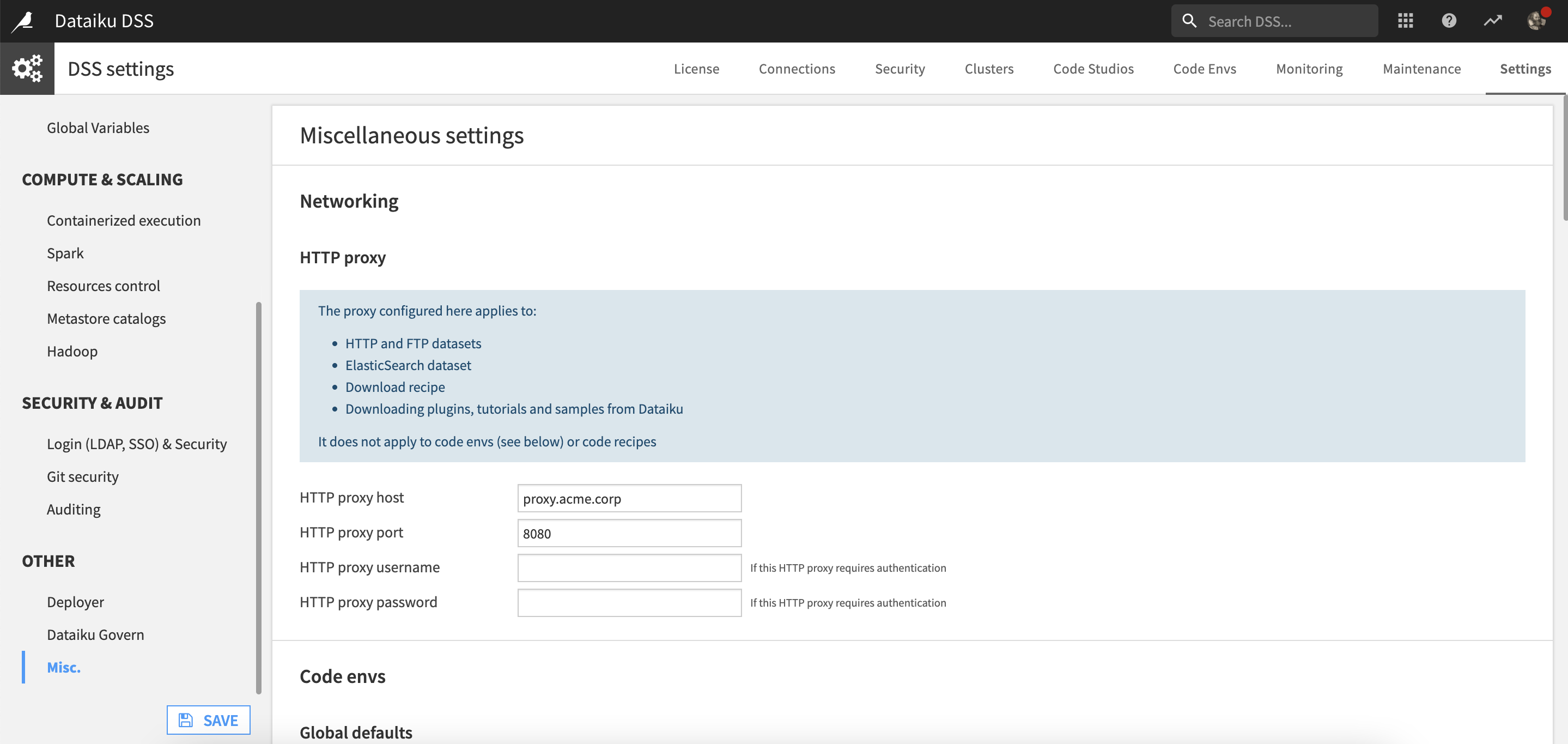
Adding the proxy settings here will route all requests initiated by the DSS backend through the proxy.
Configuring a proxy for external HTTP-based or FTP-based network resources (for remote datasets)¶
If DSS runs inside your private network, you may need to configure an outgoing proxy to allow DSS to access external HTTP- or FTP-based network resources.
This applies in particular to HTTP, HTTPS and FTP remote datasets, and Amazon S3, Google Cloud Storage, Azure Blob, Snowflake, BigQuery and Elasticsearch datasets.
You can define a global proxy configuration for DSS in the Setting tab of the Administration page. Choose Proxy, fill in the fields, and save your changes.
Every HTTP(S)- and FTP-based connection will now have an additional “Use global proxy” checkbox. Clear the checkbox if the connection should not go through the proxy (e.g., for services that are inside your private network). This also applies to Amazon S3, GCS, Azure Blob, Snowflake, BigQuery, and Elasticsearch connections.
Note
SOCKS proxies are not supported in DSS.
Warning
A note on FTP through HTTP Proxy
Connecting to a FTP server through an HTTP proxy requires passive mode, and requires
the proxy to allow and support HTTP CONNECT method on ports 20, 21 and
all unpriviledged ports (1024-65535).
Below is a sample Apache 2.4 configuration for this:
Listen 3128
<VirtualHost *:3128>
ProxyRequests On
ProxyVia On
AllowConnect 20 21 443 1024-65535
<Proxy *>
Order deny,allow
Deny from all
# IP of internal network
Allow from 1.2.3.4
</Proxy>
</VirtualHost>
Configuring a proxy for Python and R processes¶
Configuring access to external HTTP-based or FTP-based network resources only applies to native connections made from the Data Science Studio backend.
If you need to go through a proxy for network connections done from Python or R code (from a recipe or a notebook), you should configure the proxy using standard configuration directives for these environments. This includes adding explicit proxy parameters to the network calls, e.g., for Python requests:
requests.get(URL, proxies={'http', 'http://MYPROXY:MYPROXYPORT'})
and/or globally configuring proxy directives through the standard http_proxy (https_proxy, ftp_proxy …) environment variables, e.g.:
# Add the following directive to DATADIR/bin/env-site.sh
# or to the session initialization file of the DSS Unix user (.profile or equivalent)
export http_proxy="http://MYPROXY:MYPROXYPORT"
Refer to Python or R reference manuals for details.
Note
This also applies to network accesses needed to download and install additional Python or R packages.