Creating and managing Semantic Models¶
The Semantic Model editor is provided by the Semantic Models Lab plugin, which must be installed from the plugin store by an administrator
Creating a Semantic Model¶
Semantic Models are created within any Dataiku project in the Generative AI tab > Semantic Models.
It is a best practice to build semantic models on top of golden datasets.
Semantic models have a name and versions (one of which is active).
Entities¶
Entities are tables linked to business concepts and filters.
They are characterized by:
A dataset from a specific project
A name and a description
A primary key
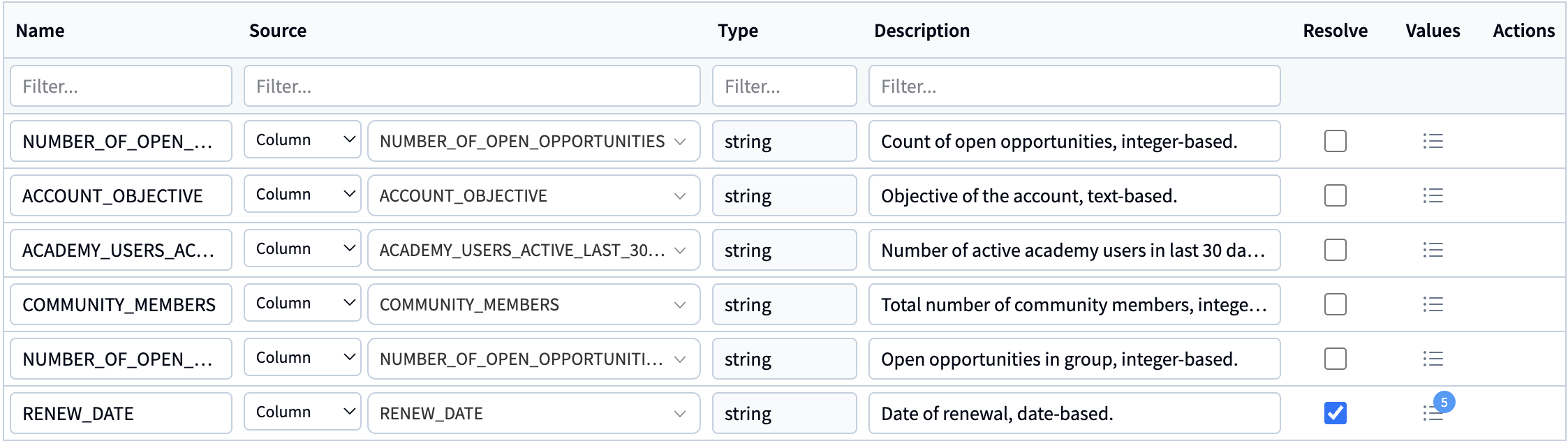
Attributes
These are mapped to columns from the dataset, come with a SQL expression (usually the column name), a type and a description
Attributes can be resolvable and have sample values
Resolvable attributes are used in a term resolution step, where the user query terms are matched to values from these attributes to account for typo corrections or schema errors
For each attribute, you can add a number of sample values (either by automatically fetching them or adding them manually)
Metrics
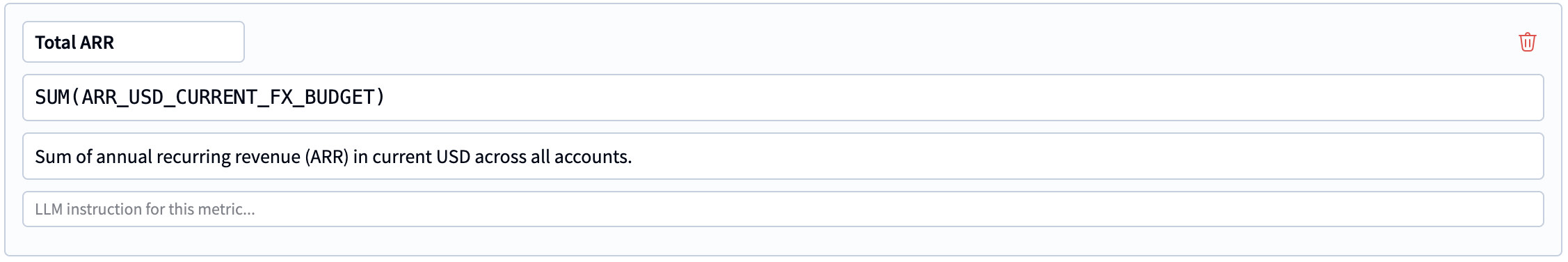
Business metrics are aggregations of attributes that can come from various entities
They come with a name, a formal SQL expression, a description and LLM instructions.
Filters
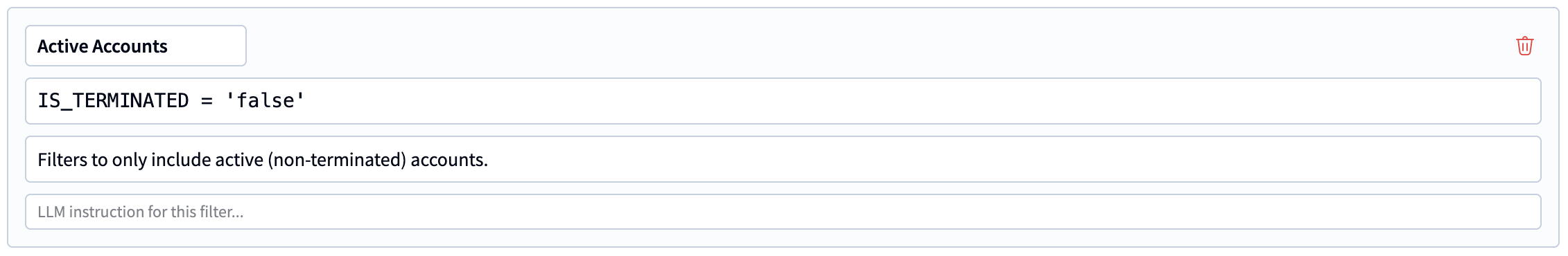
They can be used to define filters applied to columns
They come with a name, a formal SQL expression, a description and LLM instructions.
Entities can either be added manually or automatically generated using an LLM.
When using an LLM to automatically generate entities, you can specify instructions (e.g. to provide the number of entities to create from the dataset selected, how to group attributes, information on filters/metrics to create or relationships between these entities).
Automatically generating an entity takes you 80% of the way, you still need to verify and test the entity before exposing it to end-users.
Relationships¶
Relationships between entities define which keys to use to join two entities. These can both be simple and complex joins.
Glossary¶
The glossary is a collection of business specific terms. Each term comes with a name, a description and synonyms.
These terms can be added manually, or extracted from business documents (i.e. PDFs, PPTs, DOCX).
Once terms have been added to the glossary, the Used tab is used to define which terms are used in the semantic model and out of these which should be linked to entities / attributes / metrics / filters.
Golden Queries¶
Golden Queries are pre-recorded user questions and expected SQL outcomes. Providing Golden queries improves the quality of the Semantic Model Query Tool’s output.
Golden queries have names, the user question and expected SQL outcome.
These can be used for frequently asked questions or to provide guidance for complex queries.
These can be added from the Golden Queries tab or directly from the Playground.
Instructions¶
Instructions can be added, to help guide the LLM in generating the SQL - e.g. to provide specific instructions on how to deal with date attributes.
Playground¶
While creating and refining your semantic model, you can test it out in the Playground. The Playground allows you to see how your Semantic Model responds to business questions.
The Playground uses the Semantic Model Query Tool to generate and execute the SQL.
The Playground shows the LLM answer, the SQL queries executed, the records retrieved by the execution of the queries. It also shows value corrections that have been performed, as well as usage of glossary terms.
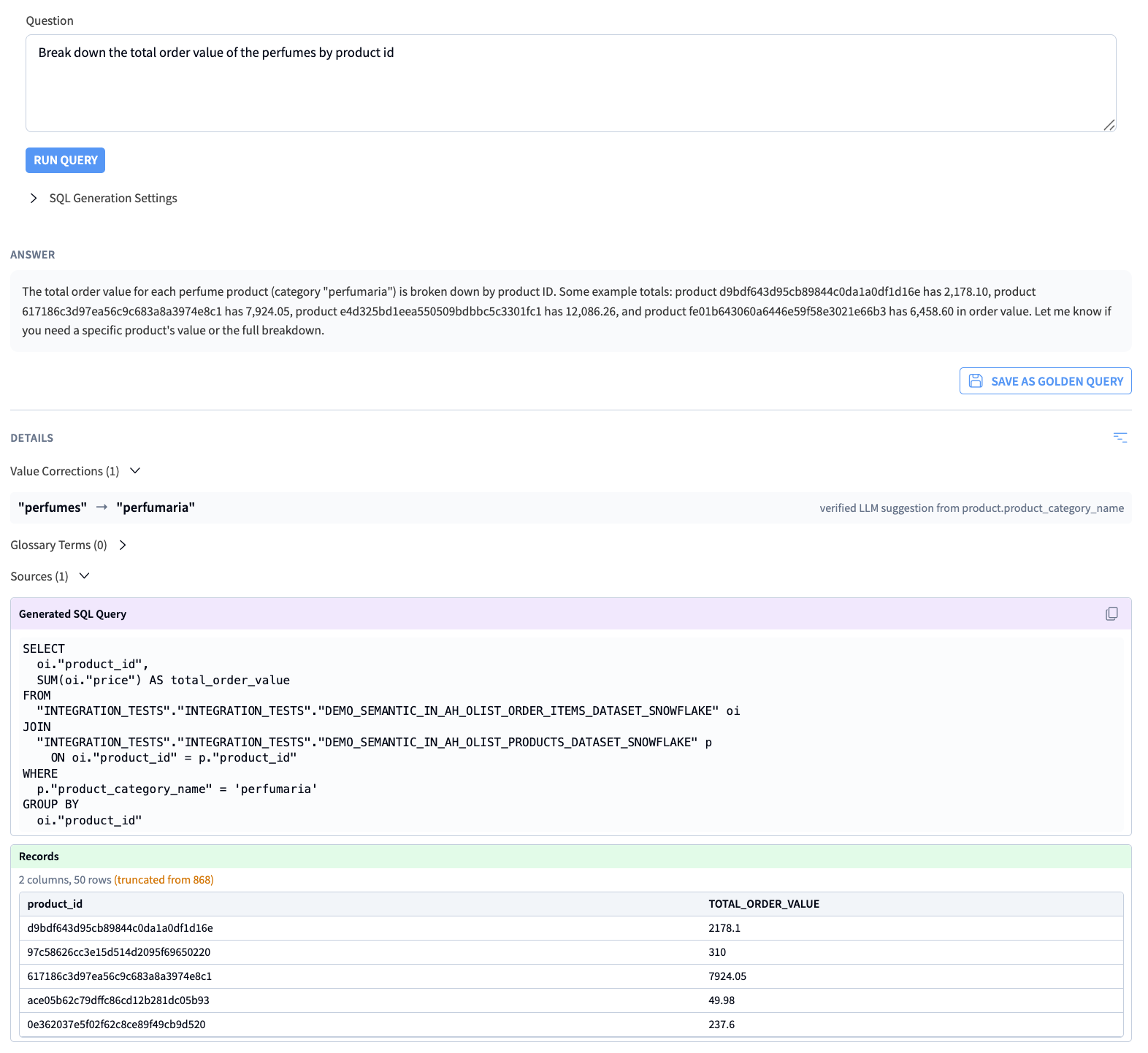
The main value of the Playground is testing out questions you are expecting end-users to ask, and using the output of the tool to refine the semantic model.
Other settings¶
The Indexing tab is where you configure and run the process that allows Dataiku to perform terms resolution and fetch sample values.
You need to specify an Embedding LLM to select the specific embedding model used for semantic resolution of attributes.
Once your settings are configured, you must manually trigger the indexing process to update the semantic model’s knowledge of your data.
Security and Permissions¶
Project Access: Users must have Read project content permissions on the project containing the Semantic Model to use it.
Data Security: Semantic Models respect underlying Dataiku dataset permissions. If a user does not have access to the underlying connection or dataset, the Semantic Search tool will fail for that user.
Versioning: Only an “Active” version of a model can be used by agents in production, ensuring that draft changes do not break existing workflows.