Creating schemas of datasets¶
Schema of new external datasets¶
When an external (“source”) dataset is created, DSS automatically detects the column names and in some case types, and automatically initializes the schema of the dataset based on the data.
Some dataset backends (like SQL databases) have strict requirements for types, while other backends can accept invalid data more easily like most text-based formats (CSV, fixed-width, JSON, …)
SQL and Cassandra datasets¶
For source datasets based on SQL or Cassandra, Data Science Studio retrieves the names and exact storage types from the SQL engine.
The schema of the dataset should generally not be edited, as the “source of truth” for the real schema is the database table.
If the schema of the underlying table changes, DSS will automatically update the schema of the dataset. However, it will only do so when you go to the edition page for this dataset. In that case, the “Save” button will be enabled. Note that this only happens if you never modified the schema of the dataset (see below)
Text-based files datasets¶
For source datasets based on text-like files without a strict schema (CSV, fixed-width, JSON, …), Data Science Studio tries to detect column names from the content and metadata of the files. Column names can be freely edited by the user.
As these files don’t include a schema restricting what kind of data can be present, Data Science Studio takes a conservative approach to typing : all columns in the generated schema will be typed as “string”, which accepts any kind of data.
There are two main usage patterns from here:
If you are sure that your data is “valid” for what you want to do with it, you can directly set the storage type, either in the dataset settings screen, or in the explore screen. The storage type will be accessible to the recipes using the dataset.
If you need to clean, enrich or preprocess your data, you can leave all storage types to “string”, and use a Data Preparation recipe to generate a clean dataset. The Data Preparation recipe will automatically generate an output dataset with precise storage types depending on the transformations defined in it. More details are available in Schema for data preparation
If the schema of the underlying data changes, DSS will automatically update the schema of the dataset. However, it will only do so when you go to the edition page for this dataset. In that case, the “Save” button will be enabled. Note that this only happens if you never modified the schema of the dataset. If you did modify the schema, you can click on the “Redetect” button to force DSS to redetect format and schema (see below).
“Typed” files datasets¶
For source datasets based on files that include a real notion of schema (Avro, Parquet, Sequence File, RC File, ORC File), the actual schema is automatically inferred when creating the dataset.
If the schema of the underlying data changes, DSS will automatically update the schema of the dataset. However, it will only do so when you go to the edition page for this dataset. In that case, the “Save” button will be enabled. Note that this only happens if you never modified the schema of the dataset. If you did modify the schema, you can click on the “Redetect” button to force DSS to redetect format and schema (see below).
Schema of managed datasets¶
In an external dataset, the “source of truth” about the dataset is the data itself. This is why, on a SQL external dataset, the schema should not be edited, as Data Science Studio implicitly trusts the SQL table. In a managed dataset, on the other hand, the user controls the schema, and defines it from the start.
When you manually create a Managed Dataset, it starts empty with an empty schema. You can then manually fill the schema in the dataset edition UI.
In most situations, you would not manually fill the schema but use the capability of the generating recipe to do it. Managed datasets are created from the recipe creation and edition UI, to be used as output of the recipe being edited.
For more information, see Handling of schemas by recipes
Modifying the schema¶
DSS never automatically modifies the schema of a dataset without an explicit user action. This is because changing the schema of a dataset can have strong consequences on all usages of the dataset.
If you hadn’t made any edit to the schema detected by Data Science Studio, it will automatically update the schema of the dataset if it notices that the underlying data files columns have changed. However, it will only do so when you go to the edition page for this dataset. In that case, the “Save” button will be enabled (in other words, while you stay on “Explore”, it will use the old schema, and detect the new schema when you go to “Settings”).
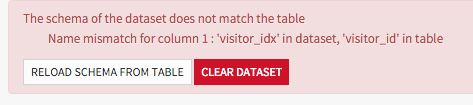
If you had manually edited the schema, Data Science Studio will notice the mismatch when you go to the edition page for this dataset and display a warning. You can then manually adapt the schema to the new data.
If at some point you modify the schema of a managed dataset while it already contains data, and the new schema does not match the existing data, Data Science Studio will notice the error and give you the option to reload the schema from the actual data, or to drop the existing data.
Each time you modify the schema, (from the dataset UI, the recipe UI or by validating a recipe), it is recommended to click on the button to check the consistency between data and schema.